Islamic State of Iraq
Salafist jihadist group in Iraq (2006-2013)
The Islamic State of Iraq (ISI; Arabic: دَوْلَةُ الْعِرَاقِ الِاسْلَامِيَّةِ Dawlat al-ʿIrāq al-ʾIslāmiyyah) was a Salafi jihadist militant organization that fought the forces of the U.S.-led coalition during the Iraqi insurgency. The organization aimed to overthrow the Iraqi federal government and establish an Islamic state ruled by Sharia law in Iraq.
| Islamic State of Iraq | |
|---|---|
| دَوْلَةُ الْعِرَاقِ الِاسْلَامِيَّةِ ad-Dawlah al-Islāmīyyah fī 'l-ʿIrāq | |
 | |
| Leaders | Abu Omar al-Baghdadi † (2006–2010) Leader Abu Ayyub al-Masri † (2006–2010) War Minister and Prime Minister Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi † (2010–2013) Leader |
| Dates of operation | 15 October 2006 – 8 April 2013[2] |
| Merger of | |
| Active regions | 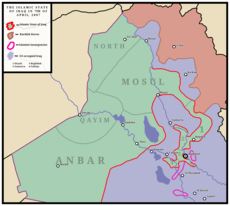 Map of the Islamic State of Iraq and its provinces on 7th of April, 2007 |
| Ideology | Salafism Qutbism |
| Allies |
|
| Opponents |
|
| Battles and wars | Iraqi insurgency (2003–2011) |
| Designated as a terrorist group by | |
Islamic State of Iraq traces its origins to Jama'at al-Tawhid wal-Jihad (JTJ) group, which was formed by the Jordanian national Abu Musab al-Zarqawi in Jordan in 1999.
References
change- ↑ Gander, Kashmira (7 July 2015). "Isis flag: What do the words mean and what are its origins?". The Independent.
- ↑ Haroro Ingram; Craig Whiteside; Charlie Winter (March 2020). "The Declaration of the Islamic State in Iraq and Sham". The ISIS Reader: Milestone Texts of the Islamic State Movement. Oxford University Press. pp. 149–160. doi:10.1093/oso/9780197501436.003.0007. ISBN 978-0-19-750143-6.
- ↑ "Islamic State: The Changing Face of Modern Jihadism" (PDF). Quilliam Foundation. November 2014. Archived from the original (PDF) on 13 November 2014. Retrieved 23 June 2015.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Hassan Hassan (13 June 2016). "The Sectarianism of the Islamic State: Ideological Roots and Political Context". Carnegie Endowment for International Peace.
- ↑ Caillet, Romain (27 December 2013). "The Islamic State: Leaving al-Qaeda Behind". Carnegie Middle East Center. Archived from the original on 20 January 2017.
- ↑ Zelin, Aaron Y. (June 2014). The War between ISIS and al-Qaeda for Supremacy of the Global Jihadist Movement (PDF). Research Notes (Report). Vol. 20. The Washington Institute for Near East Policy. Archived from the original (PDF) on 20 February 2015. Retrieved 9 February 2023.
On October 15, a statement titled "Announcing the Establishment of the Islamic State of Iraq" was released by Muharib al-Juburi, ISI's new information minister. And on November 10, AQI's replacement for Zarqawi, Abu Hamza al-Muhajir, pledged baya to the newly appointed leader of ISI, Abu Omar al-Baghdadi. ... Zarqawi's death invalidated MSM's implied pledge to bin Ladin. This means that, in effect, the group and its subsequent incarnations have not technically been subordinate to al-Qaeda in eight years.
- ↑ "Al Qaeda claims killing of 48 Syrian soldiers in Iraq". France 24. 2013-03-11. Retrieved 2021-06-21.
- ↑ "محكمة عراقية تحكم بإعدام عضوين بتنظيم "دولة العراق الإسلامية"". 23 June 2013.
- ↑ http://www.moha.gov.my/images/maklumat_bahagian/KK/kdndomestic.pdf Archived 2022-10-09 at ghostarchive.org [Error: unknown archive URL] [bare URL PDF]
- ↑ Zelin, Aaron Y. (June 2014). The War between ISIS and al-Qaeda for Supremacy of the Global Jihadist Movement (PDF). Research Notes (Report). Vol. 20. The Washington Institute for Near East Policy. Archived from the original (PDF) on 20 February 2015. Retrieved 9 February 2023.
- ↑ Zelin, Aaron Y. (June 2014). The War between ISIS and al-Qaeda for Supremacy of the Global Jihadist Movement (PDF). Research Notes (Report). Vol. 20. The Washington Institute for Near East Policy. Archived from the original (PDF) on 20 February 2015. Retrieved 9 February 2023.