4D, meaning the common 4 dimensions, is a theoretical concept in mathematics. It has been studied by mathematicians and philosophers since the 18th century. Mathematicians who studied four-dimension space in the 19th century include Möbius, Schläfi, Bernhard Riemann, and Charles Howard Hinton.
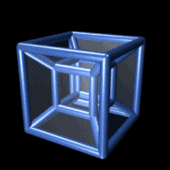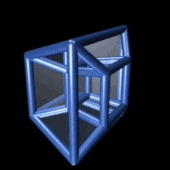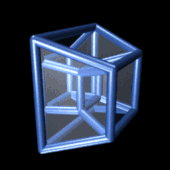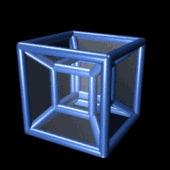
In geometry, the fourth dimension is related to the other three dimensions of length, width, and depth by imagining another direction through space. Just as the dimension of depth can be added to a square to create a cube, a fourth dimension can be added to a cube to create a tesseract.
By analogy, the universe of a 2D (two dimensional) being is a plane, but this plane may curved into a sphere. This means that if a two dimensional object goes forever forward in a straight line, the object will end up in the same position it started from. So, applying this idea to three dimensions, we can say that our universe is curved into a fourth dimension. Thus, if a three dimensional object walks forever in a straight line, the object will end up in its starting point.
Going into theoretical physics, if we look with a large enough magnification into a point in our universe, it is possible to see how the universe was many billions of years ago. It could also be possible to see small looped dimensions given high energies. The LHC and other particle colliders have tried to do that, but haven’t found any extra dimensions.
4D is also an important idea in physics, developed in the 20th century. In physics, it refers to the idea of time as a fourth dimension, added to the (3D) spatial dimensions. Albert Einstein developed the idea of spacetime by connecting space and time together. The difference is that spacetime is not a Euclidean space, but instead is called "Minkowski spacetime".
4d also has a new way to turn things, named double rotations. A double rotation is a way to turn all parts of a 4d shape except a single dot. Another completely new thing in 4d related to double rotations are isoclinic rotations, which can turn a 4d sphere kinds like turning a 2d circle. Everywhere on the sphere moves at the same speed, like with the circle.
Further reading
change- RAq2w, Paradoxy vedomi. Praha: PedF UK 1994, str. 78n
Other websites
change- The Cube shown in Five Dimensions
- [Public]