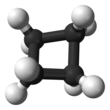
Cyclobutane is a cycloalkane organic compound with the formula (CH2)4, a colorless gas at room temperature. Cyclobutane is usually sold as a liquified gas (a gas that has been pressurized or frozen to be in a state that isn't natural). Variants of cyclobutane are called cyclobutanes. Cyclobutane has no uses in commerce or biology,[1] but compounds containing cyclobutane are important in biology and biotechnology.

| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Cyclobutane | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| Beilstein Reference | 1900183 | ||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.468 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| Gmelin Reference | 81684 | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 2601 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C4H8 | |||
| Molar mass | 56.107 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | Colorless gas | ||
| Density | 0.720 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | −91 °C (−132 °F; 182 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 12.5 °C (54.5 °F; 285.6 K) | ||
| Hazards | |||
| NFPA 704 |
| ||
| Related compounds | |||
| Related {{{label}}} | {{{value}}} | ||
| Related compounds | {{{value}}} | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Structure
changeThe carbon atoms within cyclobutane are at odd angles. Cyclobutane is unstable and will break at temperatures over about 500° celcius. Cyclobutane is connected to itself in a ladder-like structure. An example of this structure can be seen in in pentacycloanammoxic acid. This compound is a ladderane made up of five connected cyclobutane units.
References
change- ↑ "Cyclobutane - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics". www.sciencedirect.com. Retrieved 2022-03-29.