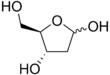
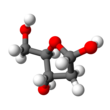
Deoxyribose is the sugar component of deoxyribonucleic acid or DNA, having one less hydroxyl group than ribose, the sugar component of ribonucleic acid or RNA.Due to its various attributes it has numerous appellations ie d-2-deoxyribose, a five carbon monosaccharide, and pentose sugar.Deoxyribose is most notable for its presence in the DNA which was first track down by a Russian-born-American biochemist Phoebus Aaron Theodore Levene (1869 – 1940) who discovered ribose (the sugar that forms the alternating backbone of RNA by binding to phosphate group) in 1909 and Deoxyribose in 1929.