Guanine is one of the five main nucleobases found in the nucleic acids DNA and RNA.
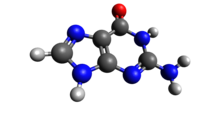
The others are adenine, cytosine, thymine, and uracil. With the formula C5H5N5O, guanine is a derivative of purine.
Basic principles
changeGuanine, along with adenine and cytosine, is present in both DNA and RNA, whereas thymine is usually seen only in DNA and uracil only in RNA.
References
change- Miyakawa, S., Murasawa, K., Kobayashi, K., Sawaoka, AB. "Abiotic synthesis of guanine with high-temperature plasma." Orig Life Evol Biosph. 30(6): 557-66, Dec. 2000.
- Horton, H.R., Moran, L.A., Ochs, R.S., Rawn, J.D., Scrimgeour, K.G. "Principles of Biochemistry." Prentice Hall (New Jersey). 3rd Edition, 2002.
- Lister, J.H. "Part II Purines." The Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds. Wiley-Interscience (New York). 1971.
Other websites
change- Computational Chemistry Wiki Archived 2007-11-01 at the Wayback Machine
- Good Guanine reference